The circulatory system is a complex network of blood vessels that plays a crucial role in supplying oxygen and nutrients to every part of our body. When this system is compromised, it can lead to various health issues, one of which is Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD). PVD is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. In this blog, we will delve into what PVD is, its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
What is Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)?
Peripheral Vascular Disease, also known as Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), is a medical condition that occurs when there is a narrowing or blockage of the blood vessels outside of the heart and brain. This condition primarily affects the arteries that supply blood to the legs and feet but can also affect arteries in the arms. PVD is a type of cardiovascular disease and is often linked to atherosclerosis, a condition in which fatty deposits (plaque) build up in the arterial walls, causing them to narrow and restrict blood flow.
Causes of Peripheral Vascular Disease
Several factors can contribute to the development of PVD, including:
- Atherosclerosis: The primary cause of PVD is atherosclerosis, where cholesterol and other fatty substances accumulate in the arterial walls, causing them to narrow and harden.
- Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for PVD, as it not only damages the blood vessels but also accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Elevated blood pressure can damage the arteries over time, increasing the risk of PVD.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of PVD due to the impact of high blood sugar levels on blood vessels.
- Age: As we age, our arteries naturally become less elastic, increasing the risk of plaque buildup and PVD.
- Family History: A family history of PVD or other cardiovascular diseases can raise your risk.
Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease
PVD often develops gradually, and its symptoms can vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Leg Pain: This is the most common symptom. It often occurs during physical activity and is relieved with rest. This pain is often referred to as “claudication.”
- Numbness or Weakness: Some people with PVD may experience numbness, weakness, or a cold sensation in their legs or feet.
- Skin Changes: Skin on the legs and feet may become pale, shiny, or discolored. Wounds or sores may take longer to heal.
- Poor Nail and Hair Growth: Reduced blood flow can lead to slower nail and hair growth on the affected limb.
- Erectile Dysfunction: In men, PVD can lead to erectile dysfunction.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Vascular Disease
The management of PVD involves lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Here are some common treatment options:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Quitting smoking, adopting a healthy diet, and regular exercise can help manage PVD and reduce symptoms.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to manage risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Antiplatelet Medications: These drugs help prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of complications.
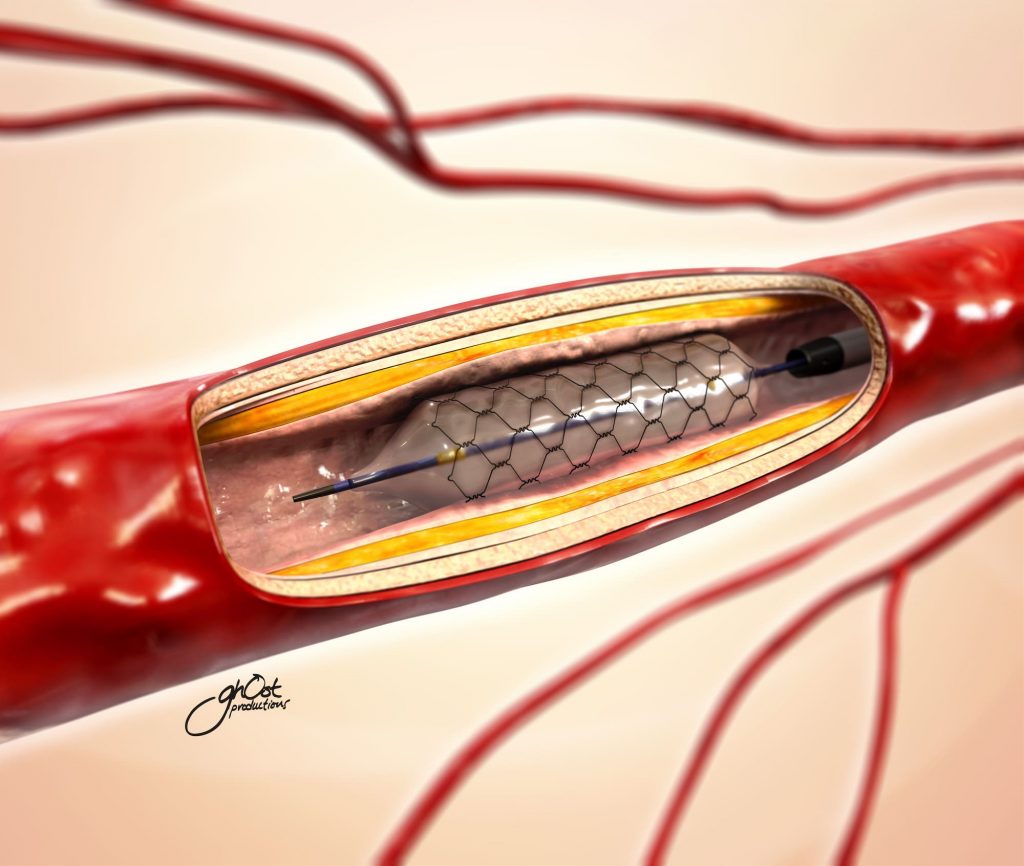
- Angioplasty and Stenting: In severe cases, procedures like angioplasty (using a balloon to widen the artery) and stenting (placing a metal mesh tube to keep the artery open) may be necessary to improve blood flow.
- Surgery: In advanced cases, bypass surgery may be performed to reroute blood flow around blocked arteries.
Conclusion
Peripheral Vascular Disease is a significant health concern that affects the quality of life of millions of people. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical management are essential in managing this condition and preventing its complications. If you or a loved one experience symptoms of PVD, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Remember, maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing and managing PVD.